- Home
- »
- Milliampere-Level Test System
Milliampere-Level Test System
Milliampere-Level Test System, the use of 24-bit high-precision ADC, TI a new generation of high-performance processors, to reach the level of 0.01% of the ultra-high accuracy, the μs level switching time to provide users with a more detailed analysis basis
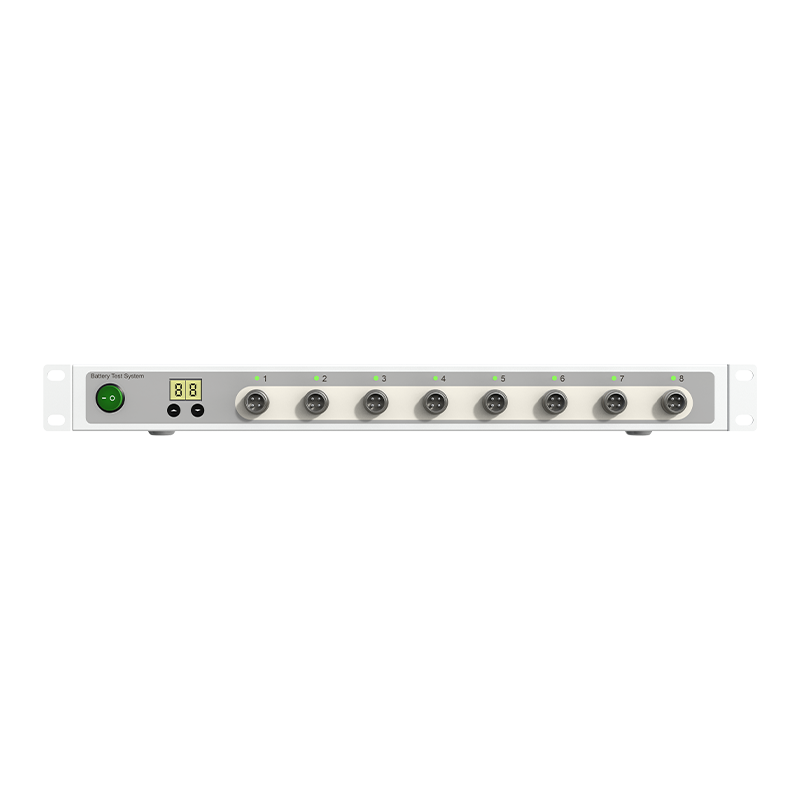
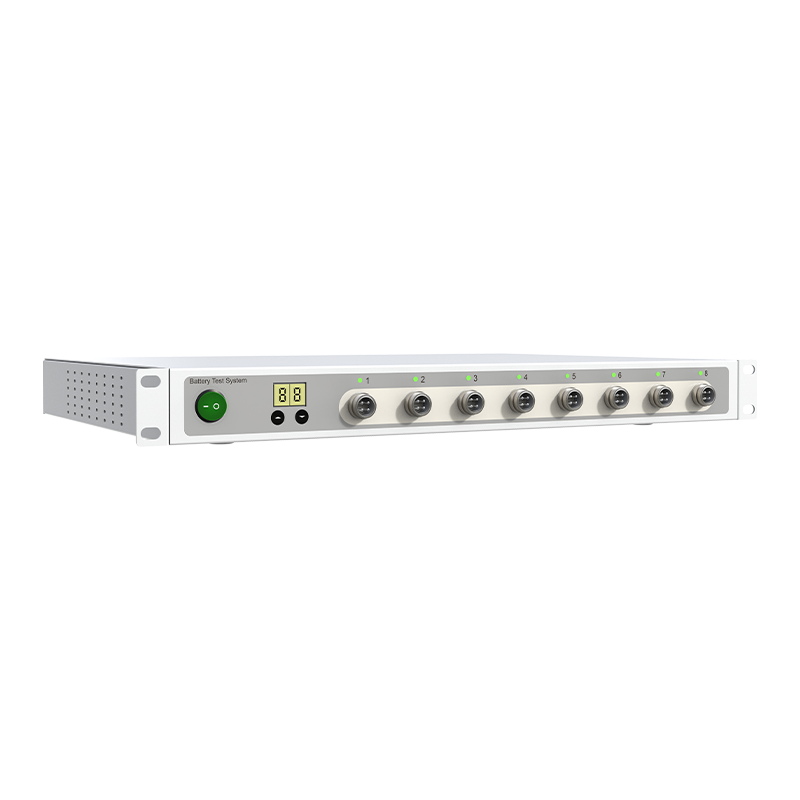




Detailed Introduction
mA class battery test system, mainly used for battery material research, high-precision test, pulse charge and discharge test, DCIR test, cycle Life test. It provides powerful testing equipment for research institutions, universities and experimental centers of battery production enterprises
System Features
Key System Parameters
Model |
BTS-5V100mA80CH |
|---|---|
Max Power | 80W |
Channels Quantity | 80CH (Customizable) |
Voltage Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Output Voltage Range | -5V~5V | |||
Voltage Accuracy | ± 0.01%F.S. | |||
Voltage Resolution | 0.001mV |
Current Parameters | |
|---|---|
Output Current Range | -100mA ~ 100mA |
Current Range | 0.1mA / 1mA / 10mA / 100mA |
Current Accuracy | ±0.02%F.S.(Current gear) |
Current Resolution | 0.001μA |
Charge And Discharge Test Parameters | |
|---|---|
Rising Time | ≤100μs |
Switching Time | ≤1ms |
Minimum Recording Time | 1ms / 0.001mV / 0.001μA |
Charge-discharge Operation Mode | CC, CV, CP, CC-CV, CR, DCIR, Pulse, etc. PITT, GITT, dQ/dV, dV/dQ, etc |
Battery voltage exceeds the upper voltage limit, confirmation time 0.2s
- Use a multimeter to measure the actual battery voltage and compare it with the voltage displayed on the BTS to check if the sample values are consistent.
- If the sample value and the actual value are not equal, confirm whether the issue is with the DC board or the wiring by swapping the sampling lines with adjacent channels. If the wiring is faulty, check for incorrect, loose, or poor connections in the voltage sampling lines.
- If the sample value and the actual value are equal, check if the upper computer step settings are reasonable and determine if the battery overvoltage occurs as soon as the step runs or at a specific point during the step.
- Check the corresponding battery for any obvious swelling, damage, or other abnormalities. If there are issues, take necessary safety measures.
- If the battery and voltage sampling lines are normal, confirm that the DC board is faulty and replace it.
Battery voltage is lower than the lower voltage limit, confirmation time 0.2s
- Use a multimeter to measure the actual battery voltage and compare it with the voltage displayed on the BTS to check if the sample values are consistent.
- If the sample value and the actual value are not equal, confirm whether the issue is with the DC board or the wiring by swapping the sampling lines with adjacent channels. If the wiring is faulty, check for incorrect, loose, or poor connections in the voltage sampling lines.
- If the sample value and the actual value are equal, check if the upper computer step settings are reasonable and determine if the battery undervoltage occurs as soon as the step runs or at a specific point during the step.
- Check the corresponding battery for any obvious swelling, damage, or other abnormalities. If there are issues, take necessary safety measures.
- If the battery and voltage sampling lines are normal, confirm that the DC board is faulty and replace it.
Module 6S does not receive data from the upper computer, switches to fault state. The fault is automatically cleared when the module receives data from the upper computer.
- Check if the module and the middle computer are in a normal powered-on state.
- Check if the CAN connection between the module and the middle computer is normal.
- Check if the CANA dip switch is set correctly.
- Measure the matching resistance between CAN H and CAN L on the CANA bus. It should be 60±5 ohms. If not, adjust the matching resistance on the signal adapter board. If the bus voltage is normal, check the BTS fault records to identify which sub-channel triggered the fault. Use debugging software tools to check if the bus voltage displayed for that channel is normal. If abnormal, it can be determined that the DC board’s bus sampling is faulty, and the board should be replaced.
- If all the above points are normal, connect a CAN box and use the captured messages to determine whether the issue lies with the middle computer or the lower computer.
Find Your Series
Our range of battery test equipment includes various specialized test systems such as the Milliampere-level Test System, IT Battery Test System, and EV Battery Test System, among others

High Performance EV Battery Test System
discharge:-6V-6V
voltage accuracy:0.02%F.S.
current accuracy:0.02%F.S.
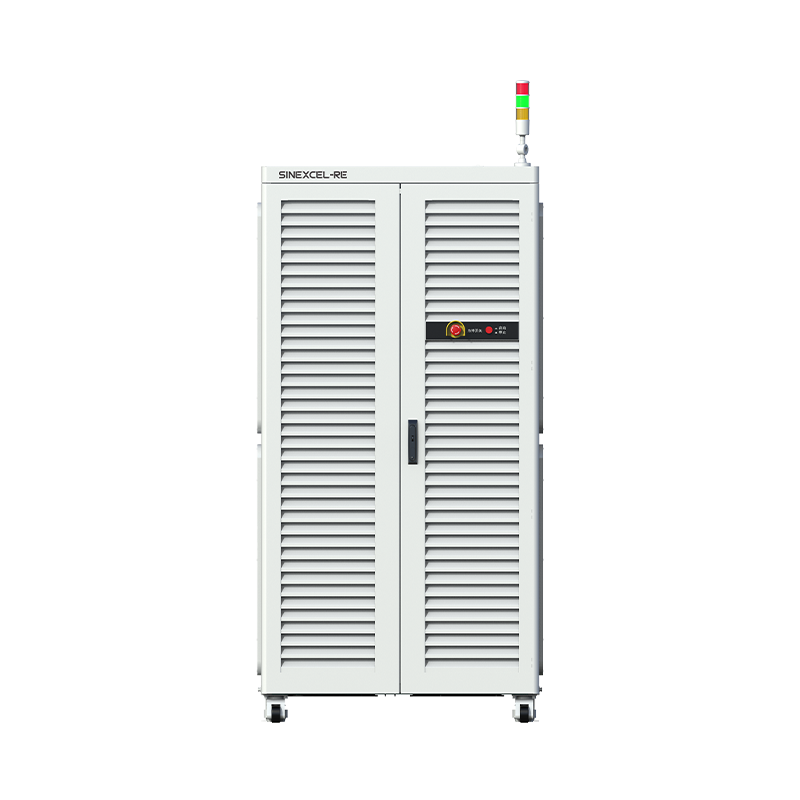
Battery Module (60v-300v) Test System
voltage accuracy:0.02%F.S.
current accuracy:0.02%F.S

Battery PACK (500v-1000v) Test System
voltage accuracy:0.02%F.S.
current accuracy:0.02%F.S.
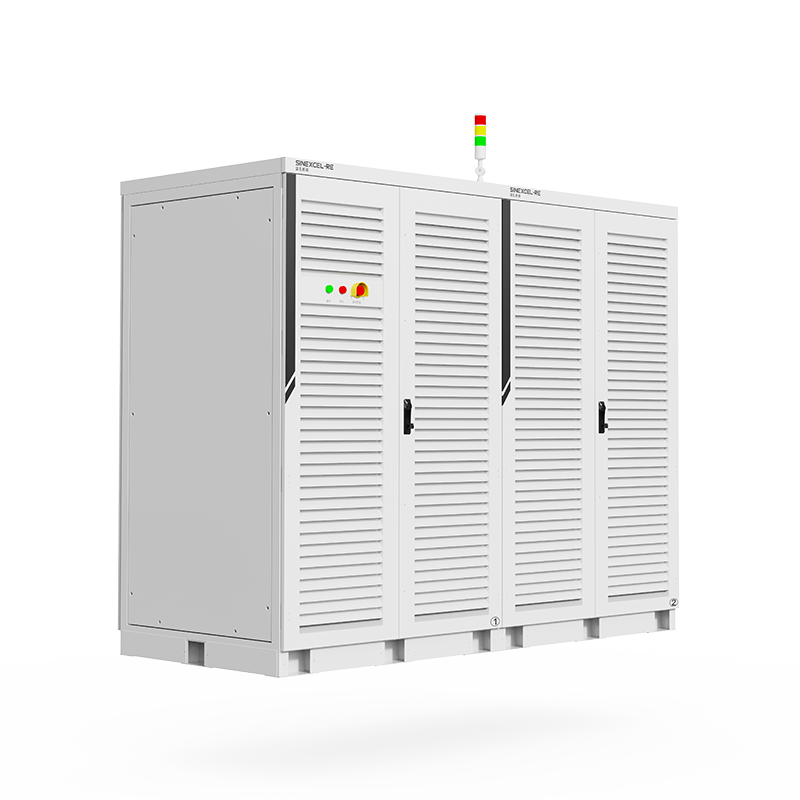
High-Volt Storage Battery Cluster Test System
voltage accuracy:0.03%F.S.
current accuracy:0.03%F.S.

Milliampere-Level Test System
discharge:-100mA~100mA
voltage accuracy:0.01%F.S.
current accuracy:0.02%F.S.

IT Battery Test System
discharge:1~5V
voltage accuracy:0.02%F.S.
current accuracy:0.05%F.S.

EV Battery Test System
discharge:1-5V
voltage accuracy:0.02%F.S.
current accuracy:0.02%F.S.
Let’S Build The Future With Innovation.
Please Provide The Following Details To Help Our Sales Representativesbetter Understand Your Needs And Get In Touch With You As Soon
